

- #Ieee 802.3 media access control layer (mac) is responsible for what? how to
- #Ieee 802.3 media access control layer (mac) is responsible for what? software
- #Ieee 802.3 media access control layer (mac) is responsible for what? iso
- #Ieee 802.3 media access control layer (mac) is responsible for what? mac
Of data information between two remote hosts (computers) attached to the same This layer has as a primary responsibility to provide error-free transmission
#Ieee 802.3 media access control layer (mac) is responsible for what? mac
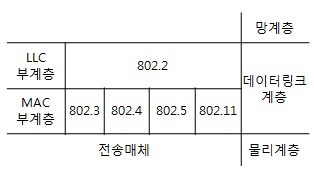
All other network interfaces will stop reading the frame when they discover that the destination address does not match their own address.Data Link Layer - MAC Sub Layer Data Link Layer Topics discussed in this tutorial: Introduction Framing HDLC protocol MAC Sublayer IEEE 802.3 Ethernet IEEE 802.5 Token Ring Introduction.
#Ieee 802.3 media access control layer (mac) is responsible for what? software
If the destination address of the frame matches with the interface address, the frame will be read entirely and be delivered to the networking software running on that computer. The medium access control mechanism is based on a system called Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD).Īs each Ethernet frame is sent onto the shared signal channel, all Ethernet interfaces look at the destination address. Access to the shared channel is determined by the medium access control (MAC) mechanism embedded in the Ethernet interface located in each station. To send data a station first listens to the channel, and when the channel is idle the station transmits its data in the form of an Ethernet frame, or packet.Īfter each frame transmission, all stations on the network must contend equally for the next frame transmission opportunity. All stations attached to an Ethernet are connected to a shared signaling system, also called the medium.
#Ieee 802.3 media access control layer (mac) is responsible for what? iso
The IEEE 802.3 physical layer corresponds to the ISO physical layer.Įach Ethernet-equipped computer operates independently of all other stations on the network: there is no central controller. (3) an Ethernet frame that consists of a standardized set of bits used to carry data over the system.Īs with all IEEE 802 protocols, the ISO data link layer is divided into two IEEE 802 sub-layers, the Media Access Control (MAC) sub-layer and the MAC-client sub-layer. (2) a set of medium access control rules embedded in each Ethernet interface that allow multiple computers to fairly arbitrate access to the shared Ethernet channel, and (1) The physical medium used to carry Ethernet signals between computers, The Ethernet System consists of three basic elements In the earliest days, 10-Mbps Ethernet war used, but now it has been extended to include a 100-Mbps version called Fast Ethernet and a 1000-Mbps version called Gigabit Ethernet. In ALOHA, the medium was the atmosphere, while in Ethernet the medium is coax cable.
#Ieee 802.3 media access control layer (mac) is responsible for what? how to
The Ethernet has its root in an early packet radio network, called ALOHA, like, the ALOHA, the problem faced by the Ethernet is how to mediate access to a shared medium fairly and efficiently. Therefore, thecarrier extension technique is used to ensure the minimum framesize of 512 bytes in Gigabit Ethernet to achieve a reasonable linkdistance.Four data rates are currently defined for operation over opticalfiber and twisted-pair cables : This restriction reducesthe efficiency drastically for high-rate transmission. The main disadvantages of the half-duplex are the efficiency and distance limitation, in which the link distance islimited by the minimum MAC frame size.
In the half duplex mode, data are transmitted using the popular Carrier-SenseMultiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) protocol on as hared medium. In the Ethernet Computer Network standard, there are two modes of operation: half-duplex and full-duplex modes. It is working examplc of the more general carrier sense multiple access with collision detect (CSMA/CD). Ethernet : IEEE 802.3 Local Area Network (LAN) Protocols : Ethernet protocols refer to the family of local-area network (LAN) technology covered by the I EEE 802.3.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
